Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central vs. SAP Business One: A Comprehensive Comparison for Key Industries
Selecting the right ERP system is critical for industries with complex operational demands, such as food, chemical, pharmaceutical, and discrete manufacturing. This blog provides an in-depth comparison of Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central and SAP Business One, focusing on their suitability for these sectors. We’ll explore feature differences, industry-specific capabilities, and real-world use cases, supported by comparative tables and actionable insights.
Industry-Specific Challenges and ERP Requirements
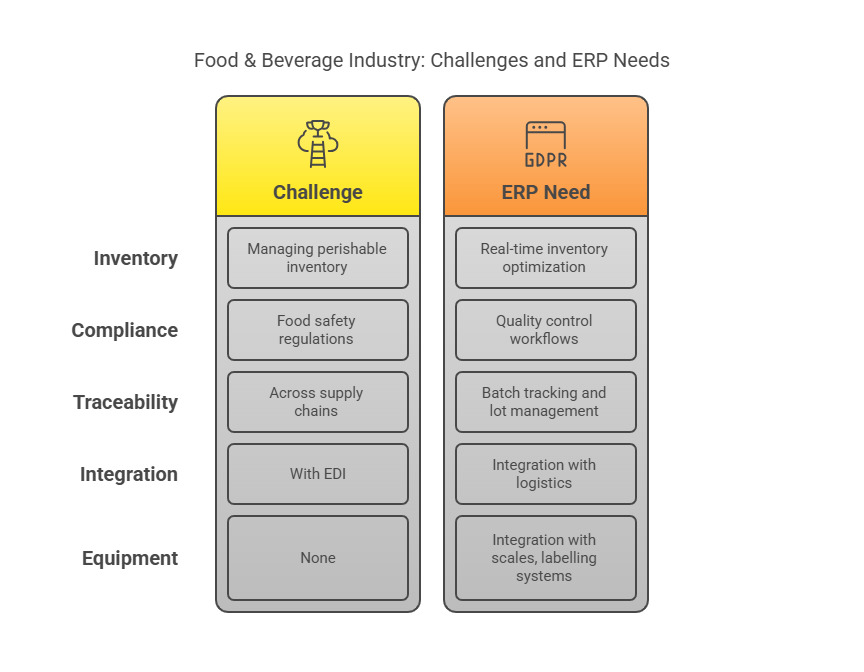
1. Food & Beverage Industry
Challenges:
Managing perishable inventory with expiry dates.
Compliance with food safety regulations (e.g., HACCP, FDA).
Traceability across supply chains.
Integration with Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) for retailer collaboration.
ERP Needs:
Batch tracking and lot management.
Quality control workflows.
Real-time inventory optimization.
Integration with scales, labelling systems, and third-party logistics.
Comparison Table: Food Industry
Feature
Traceability
Business Central-Full batch/serial tracking with expiry alerts and recall management.
SAP Business One-Basic batch tracking; limited expiry management.
Quality Control
Business Central-Automated checks, electronic signatures, and compliance dashboards.
SAP Business One-Manual quality workflows; no built-in compliance templates.
EDI Integration
Business Central-Native EDI integration for retailers.
SAP Business One-Requires third-party tools or custom development.
Inventory Optimization
Business Central-AI-driven demand forecasting and automated reordering.
SAP Business One-Static reorder points; no predictive analytics.
Microsoft’s Edge:
Dynamics Food (a Business Central-based solution) offers end-to-end traceability, integrated EDI, and quality control tailored for food safety.
Example: A food distributor uses Business Central’s expiry date tracking to reduce waste by 30% and automated EDI to cut order processing time by 50%.
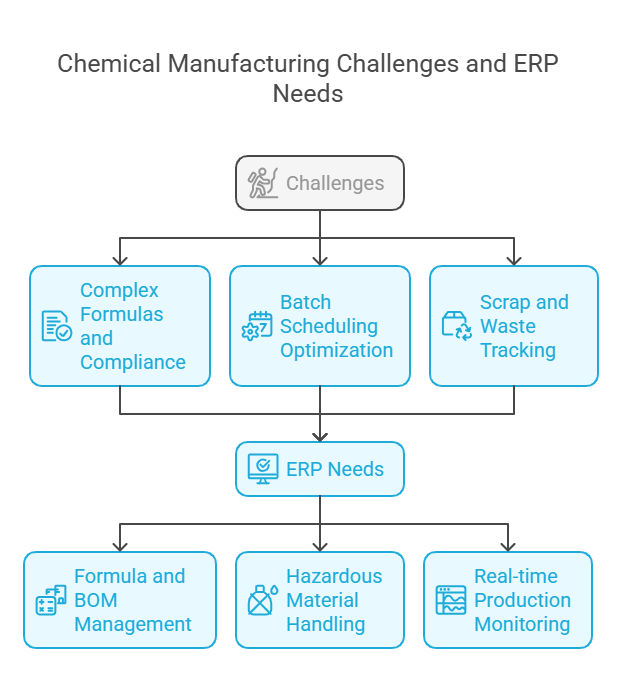
2. Chemical Manufacturing
Challenges:
Managing complex formulas and regulatory compliance (REACH, OSHA).
Optimizing batch scheduling to minimize contamination risks.
Tracking scrap and waste for sustainability reporting.
ERP Needs:
Formula and Bill of Materials (BOM) management.
Hazardous material handling and safety protocols.
Real-time production monitoring.
Comparison Table: Chemical Industry
Feature
Formula Management
Business Central-Centralized formula repository with version control and compliance checks.
SAP Business One-Basic BOM management; no formula optimization tools.
Batch Scheduling
Business Central-AI-powered scheduling to prevent cross-contamination and downtime.
SAP Business One-Manual scheduling; no contamination risk alerts.
Waste Tracking
Business Central-Scrap analysis by route, machine, or operator; sustainability dashboards.
SAP Business One-Limited scrap tracking capabilities.
Regulatory Compliance
Business Central-Automated SDS (Safety Data Sheet) generation and audit trails.
SAP Business One-Manual compliance processes.
Microsoft’s Edge:
Business Central’s AI-driven batch scheduling reduced contamination incidents by 45% for a specialty chemical manufacturer5.
Formula variants enabled a company to streamline R&D and cut time-to-market by 25%.
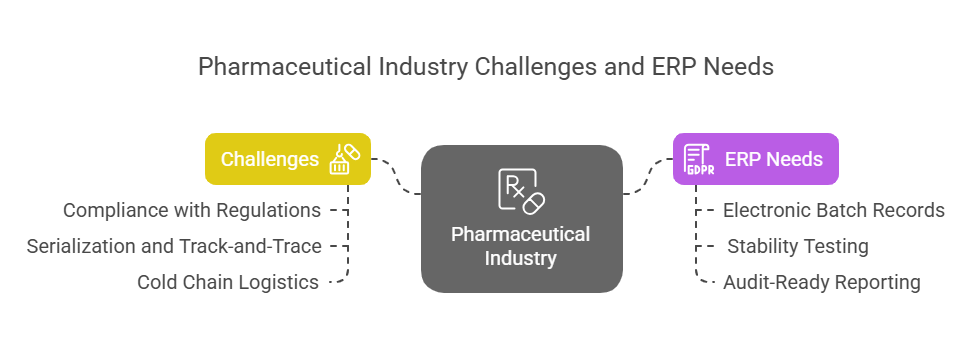
3. Pharmaceutical Industry
Challenges:
Compliance with GMP, FDA, and EU Annex 11 regulations.
End-to-end serialization and track-and-trace.
Managing cold chain logistics and sterile production environments.
ERP Needs:
Electronic batch records (EBR).
Stability testing and recall management.
Audit-ready reporting.
 Comparison Table: Pharmaceutical Industry
Comparison Table: Pharmaceutical Industry
Feature
Serialization
Business Central-Full serial number tracking from raw materials to patient.
SAP Business One-Limited serialization; no integration with track-and-trace systems.
Quality Management
Business Central-Automated stability testing, deviation management, and electronic signatures.
SAP Business One-Manual quality workflows; no EBR support.
Cold Chain Management
Business Central-Temperature monitoring and automated alerts for logistics partners.
SAP Business One-No native cold chain features.
Regulatory Reporting
Business Central-Pre-configured FDA/EU reports and audit trails.
SAP Business One-Custom reports require developer input.
Microsoft’s Edge:
A mid-sized pharma company used Business Central’s electronic signatures to reduce audit preparation time by 60%.
Power BI integration provided real-time dashboards for batch yield analysis, improving production efficiency by 20%.
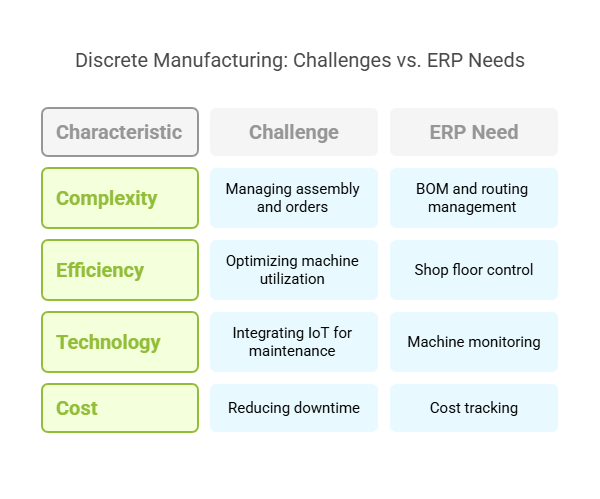
4. Discrete Manufacturing
Challenges:
Managing complex assembly processes and custom orders.
Optimizing machine utilization and reducing downtime.
Integrating IoT for predictive maintenance.
ERP Needs:
Multi-level BOM and routing management.
Shop floor control and machine monitoring.
Cost tracking for make-to-order (MTO) scenarios.
Comparison Table: Discrete Manufacturing
Feature
Production Planning
Business Central-Finite scheduling with machine learning-driven resource allocation.
SAP Business One-Basic MRP; no AI optimization.
IoT Integration
Business Central-Native Azure IoT Hub connectivity for predictive maintenance.
SAP Business One-No built-in IoT support; third-party tools required.
Cost Tracking
Business Central-Real-time cost accumulation by job, machine, and labor.
SAP Business One-Post-production cost analysis only.
Customization
Business Central-Low-code workflows via Power Platform; 500+ AppSource extensions.
SAP Business One-Limited customization; requires SAP partner support.
Microsoft’s Edge:
An automotive parts manufacturer used Business Central’s IoT integration to reduce machine downtime by 35% through predictive maintenance7.
Power Apps enabled a custom assembly tracking system, cutting production errors by 50%8.
Key Differentiators: Business Central vs. SAP Business One
1. Integration and Ecosystem
Business Central: Seamless integration with Microsoft 365, Teams, Power BI, and Azure services. Example: Teams integration allows production managers to approve purchase orders directly from chat.
SAP Business One: Relies on third-party tools for advanced integrations (e.g., CRM, BI).
2. Scalability and Pricing
Business Central: Subscription-based pricing ($8–$100/user/month) with unlimited cloud scalability.
SAP Business One: Perpetual licensing & Subscription Licensing with higher upfront costs; limited cloud flexibility.
3. User Experience
Business Central: Modern UI with role-based dashboards and Microsoft Fluent Design38.
SAP Business One: Outdated desktop interface; steep learning curve.
4. Future-proofing
SAP plans to phase out Business One support, while Microsoft invests heavily in Business Central’s AI and IoT capabilities.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central outperforms SAP Business One in food, chemical, pharmaceutical, and discrete manufacturing industries due to its:
Industry-specific modules (e.g., Dynamics Food, chemical formula management).
Superior integration with modern tools like Power BI, Teams, and Azure IoT.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness for growing businesses.
For companies prioritizing innovation, compliance, and long-term growth, Business Central is the clear choice. SAP Business One remains viable only for organizations with static, on-premises requirements and simpler workflows.
Need help choosing? Contact our experts for a free ERP assessment tailored to your industry.